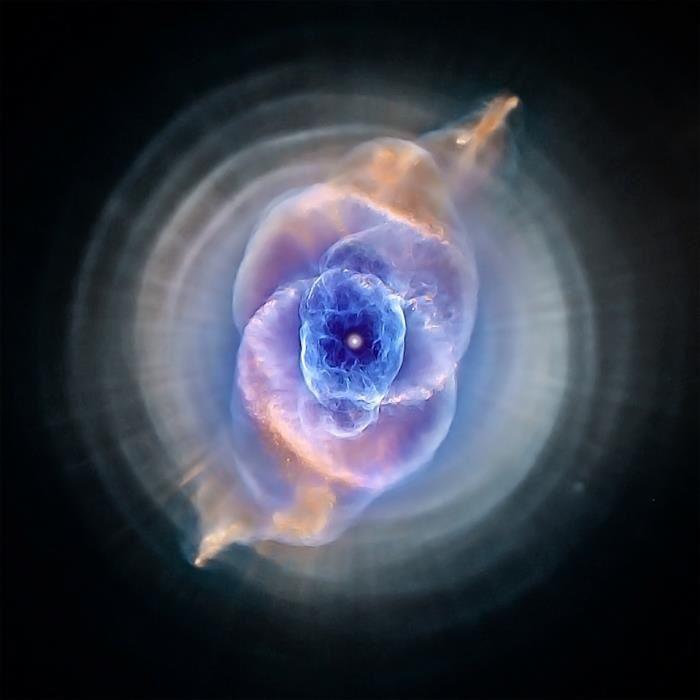

Cats Eye Nebula
Some of the amazing known Nebulae
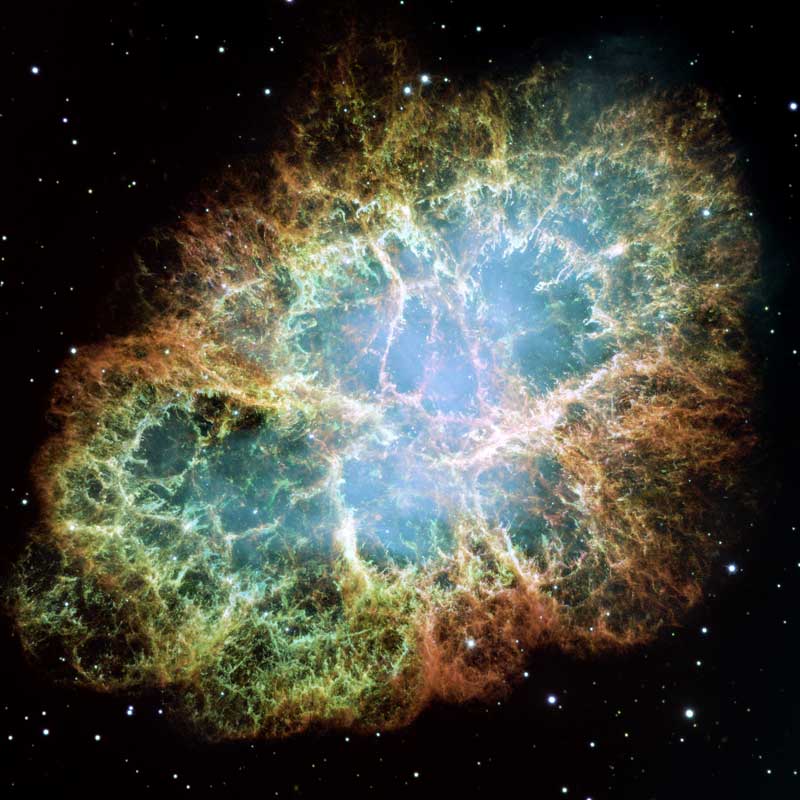
Crab Nebula

Butterfly Nebula
Nebulae are the places where stars are born, So it's a place where things starts
A nebula is a giant cloud of dust and gas in space. Some nebulae (more than one nebula) come from the gas and dust thrown out by the explosion of a dying star, such as a supernova. Other nebulae are regions where new stars are beginning to form.

Cats Eye Nebula

Crab Nebula

Butterfly Nebula
The Cat's Eye Nebula or
NGC 6543,
is a relatively bright planetary nebula in the
northern constellation of Draco,
discovered by William Herschel
on February 15,
1786.
The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant in the
constellation of Taurus.
The current name
is due to William Parsons,
3rd Earl of Rosse,
who observed the object in 1840 and
produced a drawing that looked somewhat like a crab.
NGC 6302, also called the Bug Nebula or
Butterfly Nebula,
is a bipolar planetary nebula
in the
constellation Scorpius.
The structure in the nebula is among the
most complex
ever observed in planetary nebulae.



A spiral galaxy like the Milky Way contains stars, stellar remnants, and a diffuse interstellar medium (ISM) of gas and dust. The interstellar medium consists of 10−4 to 106 particles per cm3 and is typically composed of roughly 70% hydrogen by mass, with most of the remaining gas consisting of helium. This medium has been chemically enriched by trace amounts of heavier elements that were ejected from stars as they passed beyond the end of their main sequence lifetime. Higher density regions of the interstellar medium form clouds, or diffuse nebulae, where star formation takes place. In contrast to spirals, an elliptical galaxy loses the cold component of its interstellar medium within roughly a billion years, which hinders the galaxy from forming diffuse nebulae except through mergers with other galaxies.

.png)
.png)
.png)
Stars go to supernova and forms the beautifull places in the universe, but not all stars are
capable to go for a boom. Only the bigger ones,
So is our sun capable to form a nebula? Well studies says yes,
OUR SUN WILL
DIE IN STYLE
Here's how our beloved sun is going to die...
 First it will expand and expand as a red
giant then will form a supergiant and that time we will not find any sunset or sunrise
instead we will find ourselves inside of our sun. Is'nt it amazing?
First it will expand and expand as a red
giant then will form a supergiant and that time we will not find any sunset or sunrise
instead we will find ourselves inside of our sun. Is'nt it amazing?
Thereafter after our sun will become a white dwarf earth sized super dense with dust and
gas surrounding and
that's the nebula formed by our sun
So cycle is like
Nebulas are destroyed by the stars they create. Yes most beautiful, favourite, famous nebulas
will also die
Nebulas are pillars of creation but one day they will be just clusters of
stars.
"That will be just a beginning and not the end. It will form another solar system
like ours or Even better, who knows"









An H2 region nebula,It is situated in the Milky Way, one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky.
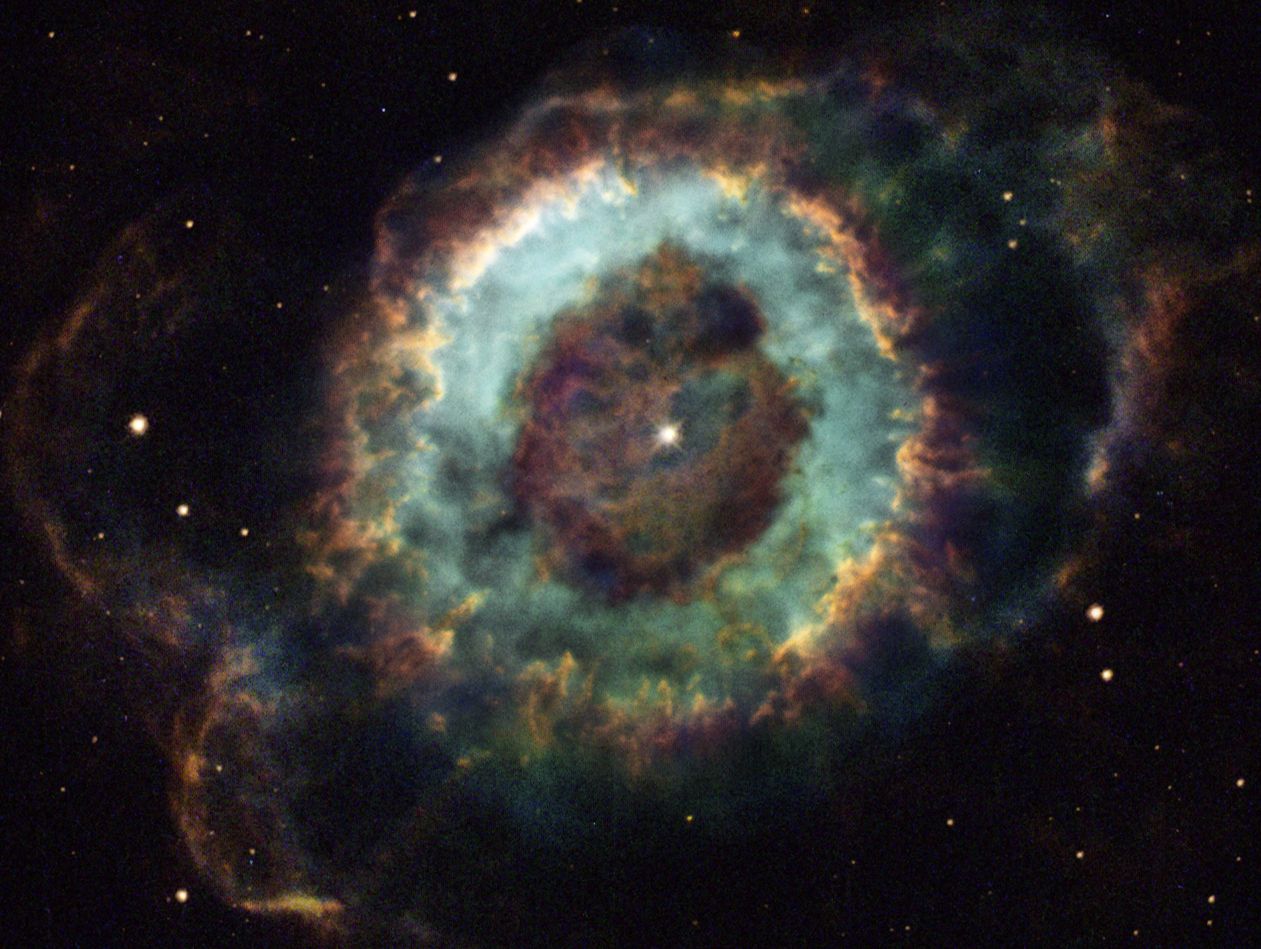

A planetary nebula, was discovered by William Herschel Round and planet-shaped, the nebula is also
relatively faint.

A reflection nebula, an extremely faint reflection nebula believed to be an ancient supernova remnant or
gas cloud

A supernova remanant, In the year 1054 it apears as a new star and was visible in the broad daylights 10 times brighter than Venus and it apears for 29 days, it is 6300 light years awy from our solar system, today we can see it only through telescope


.png)
.png)
.png)

A Dark nebula,The Horsehead Nebula is approximately 460 parsecs or 1400 light years from Earth.[1] It is one of the most identifiable nebulae because of its resemblance to a horse's head. The nebula was first recorded in 1888 by Scottish astronomer Williamina Fleming


.png)
.png)
.png)
Using the National Science Foundation's Robert C. Byrd Green Bank Telescope, radio astronomers have found that Smith's cloud has a mass of at least one million solar masses and measures 3,000 parsecs (9,800 ly) long by 1,000 pc (3,300 ly) wide in projection.[5] The cloud is between 11,100 pc (36,000 ly) and 13,700 pc (45,000 ly) from Earth[5] and has an angular diameter of 10 to 12 degrees, approximately as wide as the Orion constellation, or about 20 times the diameter of the full moon, although the cloud is not visible to the naked eye.
